An overview of CoreWeave: Part 1 (Competitive Landscape, Business Model and Financials)
A brief overview of the Business of CoreWeave
On Friday, 28th of March 2025, cloud computing company CoreWeave, which specializes in GPU-accelerated cloud infrastructure, went public.
This IPO represents a pivotal moment in the generative AI boom, marking the first public debut of a company that rose to prominence by capitalizing on the explosion of AI workloads. Positioned as a specialized provider of GPU-accelerated cloud infrastructure, CoreWeave has benefited from its strategic focus on high-performance computing for AI applications, as well as its deep partnership with NVIDIA.
However, its muted IPO debut—raising $1.5 billion at a valuation of $14 billion, far below initial expectations—reveals both the opportunities and challenges facing AI-focused infrastructure providers. The IPO highlights the insatiable demand for AI computation, with marquee customers like Microsoft and OpenAI validating CoreWeave's business model. Yet, it also underscores the risks of heavy debt, customer concentration, and fierce competition from hyperscalers like AWS and Azure. For investors, CoreWeave's public listing is a bellwether for how markets will assess the sustainability of AI-driven growth amidst broader economic volatility and skepticism about overhyped valuations. This is not just a financial milestone for CoreWeave but a test case for the viability of pure-play AI infrastructure companies in public markets.
Let’s briefly go through the origins of CoreWeave. It began in 2017 as Atlantic Crypto, focused on Ethereum mining. This origin story matters because it gave them early experience handling massive GPU deployments efficiently. When they pivoted to cloud computing, they brought along this specialized knowledge that most traditional cloud providers simply didn't have.
What sets CoreWeave apart is how deeply they've leaned into this specialization. While hyperscalers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer broad, general-purpose cloud services, CoreWeave focuses specifically on GPU-accelerated infrastructure tailored for compute-intensive workloads such as AI, machine learning, and high-performance computing.
Industry and Competitors
Now, let’s take look at the industry and the strategic group* within the industry that CoreWeave operates in.
CoreWeave belongs to the Cloud Computing Industry, specifically within the Cloud GPU Services Strategic Group. This strategic group focuses on providing GPU-accelerated cloud infrastructure for compute-intensive workloads like AI, machine learning, and high-performance computing.
CoreWeave competes directly with several specialized GPU-focused cloud providers. The following companies belong to the same Strategic Group as CoreWeave and, hence, they are CoreWeave’s direct rivals:
Lambda: Focuses on multi-GPU instances optimized for training large language models and other machine learning tasks
Cerebras: Offers unique hardware like the Wafer-Scale Engine for high-performance computing scenarios, including natural language processing and scientific simulations
Aethir: Provides decentralized GPU cloud services as an alternative to centralized providers like CoreWeave, catering to smaller AI startups with cost-effective solutions
CoreWeave operates in this sub-group of cloud providers that specialize in GPU-accelerated services, differentiating itself from general-purpose cloud providers i.e. AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform by focusing on high-performance GPUs for AI workloads.
Business Model
What’s the target market for Core Weave and who are CoreWeave’s primary existing customers?
CoreWeave’s AI-optimized cloud infrastructure is designed for companies that require high-performance, scalable, and cost-efficient GPU compute for demanding workloads. Its ideal customers include:
1. AI/ML Startups & Scaleups
Companies training or fine-tuning large language models (LLMs), diffusion models, or other generative AI systems
Startups needing fast access to the latest GPUs (H100, H200, GB200) without long-term hardware commitments
Teams that want to avoid managing their own data centers but still need hyperscale-level performance
2. Enterprise AI Labs & Big Tech
Tech giants (like Microsoft, Meta, OpenAI) running large-scale AI training and inference
Companies requiring massive GPU clusters with ultra-low-latency networking and high-throughput storage
Businesses that need long-term, reserved capacity (2–5 year contracts) for stable AI workloads
3. AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) Providers
Companies offering AI APIs, model hosting, or real-time inference services
Firms that need high-uptime, scalable infrastructure to serve enterprise clients
4. Research Institutions & Universities
AI labs running cutting-edge research (e.g., drug discovery, climate modeling, robotics)
Academic institutions that need burst capacity for large experiments without maintaining their own supercomputers
5. High-Performance Computing (HPC) Users
Industries like biotech, financial modeling, and autonomous vehicles that rely on GPU-accelerated computing
Companies running simulations, rendering, or complex data processing
Current Customers of CoreWeave
Infrastructure and technology providers –MSFT, Meta, NVIDIA, IBM
Hedge fund Jane Street
Key pain points that CoreWeave's Current and Potential Customers Face
AI companies today face significant challenges when it comes to infrastructure. Traditional cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud weren’t designed for AI workloads, leading to inefficiencies where GPU clusters often operate at just 35-45% of their potential capacity—meaning businesses waste money on underutilized resources. Additionally, accessing the latest AI hardware, such as NVIDIA’s cutting-edge H100, H200, and GB200 GPUs, can take months or even years through conventional cloud providers, slowing down critical AI development. The high costs of running AI at scale, combined with the complexity of managing clusters—requiring manual tuning, burn-in testing, and constant monitoring—further drain time and resources.
How Does CoreWeave Solve Them?
CoreWeave solves these problems with a cloud platform purpose-built for AI. By optimizing every layer of the stack, CoreWeave delivers up to 20% higher efficiency than hyperscalers, ensuring customers get more performance for their investment. The company rapidly deploys the latest GPUs, often within weeks of their release, giving AI teams a competitive edge. With fully automated provisioning, clusters are ready in hours—eliminating manual setup and reducing costs. CoreWeave’s infrastructure is designed for scale, featuring bare-metal GPUs, ultra-fast networking (2GB/s per GPU), and high-performance storage, all monitored by its Mission Control system to prevent downtime. Unlike general-purpose clouds, CoreWeave allows training and inference workloads to run simultaneously on the same cluster, maximizing utilization. Ultimately, CoreWeave removes the infrastructure barriers holding back AI innovation, letting companies focus on building the next generation of AI models.
CoreWeave's Revenue Model
CoreWeave primarily generates revenue by providing AI-optimized cloud infrastructure and managed services through its CoreWeave Cloud Platform. The company operates on a usage-based pricing model:
Compute resources (GPU/CPU capacity) are billed per GPU per hour
Storage is priced separately per gigabyte per month
Additional revenue comes from proprietary software services (managed Kubernetes, orchestration tools, and AI workload optimization solutions)
A key differentiator is CoreWeave’s contract structure: 96% of revenue comes from long-term commitments (2–5 years) with enterprise customers, ensuring predictable, recurring revenue. This model provides high visibility into future earnings while allowing clients to secure capacity for demanding AI workloads at scale.
By combining flexible, usage-based pricing with sticky multi-year contracts, CoreWeave aligns its revenue with the growing demand for high-performance AI infrastructure.
Growth Strategy (How do they plan to expand and acquire new customers?)
CoreWeave’s strategy is clear: dominate AI infrastructure by being faster, more efficient, and more adaptable than hyperscalers.
1. Enhance its cloud platform
The company has already deployed some of the world’s largest GPU clusters, optimized for AI workloads, and continues to enhance its cloud platform with proprietary software like CKS (managed Kubernetes for AI), Mission Control (infrastructure monitoring), and SUNK (Slurm on Kubernetes). By investing heavily in R&D, CoreWeave ensures its infrastructure delivers better performance, efficiency, and cost savings than generalized hyperscalers—keeping it ahead in the AI arms race.
2. Expanding Within Existing Customers
CoreWeave’s client base includes leading AI labs, big tech firms, and enterprises that rely on its platform for large-scale training and inference. As these customers scale their AI deployments, CoreWeave benefits from organic growth—more GPUs, longer contracts, and deeper integrations. The company has dedicated AI-focused teams working closely with clients to tailor solutions, ensuring it captures an increasing share of their AI spend.
3. Entering New Industries & Verticals
While CoreWeave’s early adopters were AI-native companies, the next wave of growth will come from traditional industries adopting AI at scale. Sectors like finance (high-frequency trading), healthcare (drug discovery), and manufacturing (predictive maintenance) are beginning to build custom AI solutions. CoreWeave is actively targeting these markets, anticipating a surge in demand as AI becomes ubiquitous across the economy.
4. Global Expansion
AI compute isn’t just a U.S. phenomenon—companies worldwide need low-latency, regionally compliant infrastructure. CoreWeave has already expanded into Europe (UK, Sweden, Spain) and Canada, with plans to grow further. Data sovereignty laws and latency requirements mean AI models must often be trained and served locally, creating a long-term opportunity for CoreWeave to establish a global footprint.
5. Vertical Integration: Moving Up & Down the Stack
To lock in its competitive edge, CoreWeave is pursuing vertical integration in two directions:
Up the Stack: Adding higher-level AI tools (e.g., inferencing APIs, fine-tuning solutions) to make its platform more accessible.
Down the Stack: Increasing control over data centers—potentially through acquisitions—to reduce costs and accelerate deployment timelines.
6. Maximizing Infrastructure Lifespan
GPUs don’t become obsolete overnight. CoreWeave optimizes its fleet by repurposing older chips for inference or less intensive workloads once training contracts expire. This extends the economic life of its hardware while offering lower-cost options for customers with varying compute needs.
Financials
Let me begin with the numbers:
Revenue Growth:
2022: $15.83M
2023: $228.94M (+1,346% YoY)
2024: $1.91B (+737% YoY)
Profitability: Still deep in the red
2022 Net Loss: ($31M), 194% of revenue
2023 Net Loss: ($594M), 259% of revenue
2024 Net Loss: ($863M), 45% of revenue
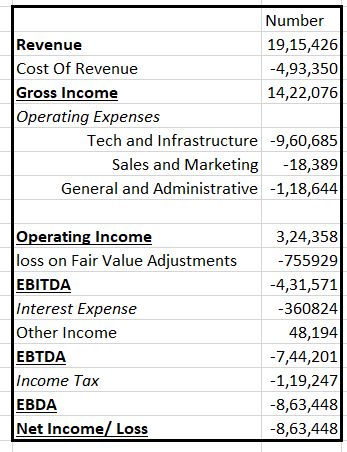
Below is a detailed breakdown for FY 2024
Now let’s interpret these numbers.
CoreWeave’s business model is built around renting GPU-powered infrastructure to AI labs and enterprises, with a pricing structure that charges customers on a per-GPU-per-hour basis for compute power and separately for storage. This model has proven lucrative, with gross margins of approximately 74% in 2024, reflecting the profitability of GPU cloud services before accounting for heavy overhead costs.
CoreWeave’s underlying operations are robust on a cash basis. Excluding non-cash expenses like depreciation, the company achieved an adjusted EBITDA margin of 62% in 2024, highlighting strong unit economics when its GPU hardware is fully utilized.
However, the company’s ambitious growth strategy has come at a significant cost. CoreWeave’s business model is emblematic of the capital-intensive nature of AI infrastructure providers. Its expenses on Technology and Infrastructure are almost 50% of its total Revenue.
The other major area that’s eating away from its revenue is losses on fair value adjustments. A loss on fair value adjustments happens when an asset's value, as determined by the market (fair value), falls below its recorded value (book value), resulting in a loss for the company. The idea is kind of similar to Depreciation but there are some nuances.
A brief note on fair value adjustments
What it is:Fair value adjustments are made to reflect the current market value of an asset, which might be higher or lower than its original cost or book value.
When they occur:
They happen when there's a change in the market conditions or circumstances that affect the asset's value.
Example:
Imagine you own a piece of land. If the market value of similar land drops significantly, you might need to adjust the value of your land to reflect this lower market price.
Loss on Fair Value Adjustment:
If the fair value adjustment results in a lower value than the asset's book value, that's a loss on fair value adjustment.
Accounting:
This loss is recognized in the income statement, reducing the company's profit.
With 250,000 GPUs deployed across 32 data centers by the end of 2024, CoreWeave has positioned itself as one of the few players capable of meeting the global shortage of high-end GPUs needed for AI workloads. However, this rapid scaling has exposed vulnerabilities: customer concentration risks (Microsoft alone accounts for 62% of revenue), dependence on Nvidia for hardware supply, and exposure to fluctuating demand for AI investments.
Ultimately, CoreWeave’s IPO is more than just a financial event—it is going to be a indicator for how public markets will value companies that underpin the generative. This IPO is not just a financial milestone for CoreWeave but a test case for the viability of pure-play AI infrastructure companies in public markets.
In Part 2, we will cover the Technology behind CoreWeave’s offerings in details.
REFERENCES and SOURCES for FURTHER EXPLORATION
CoreWeave’s SEC Form S-1: https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1769628/000119312525044231/d899798ds1.htm